Vendor Management Best Practices for 2025: Boost Your Strategy
Learn top vendor management best practices for 2025 to streamline processes, reduce risks, and maximize vendor value effectively.

In today's interconnected business environment, your vendors are more than just suppliers; they're extensions of your team and crucial partners in your success. Managing these relationships effectively can mean the difference between simply operating and truly thriving. But how do you move beyond basic transactions to build a robust, strategic vendor ecosystem that adds real value to your bottom line? It starts with implementing proven vendor management best practices.
This guide cuts straight to the point. We'll break down seven essential strategies that will help you reduce risk, enhance performance, and unlock significant cost savings. We'll provide actionable steps for each practice, showing you how to transform your vendor management from a simple administrative task into a powerful competitive advantage.
From initial due diligence and strategic segmentation to performance monitoring and building genuine partnerships, you'll gain practical insights to immediately apply. Plus, we'll highlight how modern automation tools like Tailride can eliminate the manual burdens of invoice and receipt processing. This frees up your team to focus on what really matters: building strong, strategic relationships that drive your business forward. Let’s dive into the practices that create a world-class vendor management program.
1. Vendor Risk Assessment and Due Diligence
Effective vendor management best practices begin long before a contract is ever signed. A thorough vendor risk assessment and due diligence process is your first line of defense, acting as a systematic screening to evaluate potential partners. This involves a deep dive into a vendor's financial health, security protocols, operational capabilities, and compliance with industry standards to identify and mitigate potential risks from the outset.

Think of it like a background check for your business partners. By scrutinizing vendors before onboarding, you protect your company from financial instability, data breaches, and reputational damage. This proactive approach ensures that the vendors you choose are not only capable but also secure and reliable, setting the foundation for a successful long-term relationship.
Real-World Examples
- •JPMorgan Chase: The financial giant runs a comprehensive vendor risk program that vets over 50,000 vendors annually, ensuring every partner meets its stringent security and compliance requirements.
- •Walmart: Its supplier assessment program goes beyond operations, evaluating vendors on crucial factors like sustainability, ethics, and labor practices to uphold its corporate values across the supply chain.
How to Implement This Practice
- •Develop Standardized Criteria: Create a scoring matrix with clear, consistent criteria for all potential vendors. This ensures fair and objective evaluations.
- •Tier Your Assessments: Not all vendors pose the same level of risk. Classify them into tiers (e.g., high, medium, low risk) based on their criticality to your operations and their access to sensitive data. High-risk vendors should undergo a more rigorous assessment.
- •Automate Screening and Monitoring: Use tools to automate initial background checks and continuously monitor vendors for any changes in their risk profile, such as negative news or financial instability.
- •Maintain a Risk Register: Keep an updated register of all vendor risks and review it quarterly. This helps you stay prepared and ensures that your documentation is always audit-ready. For more guidance on this, explore our detailed post on how to prepare for an audit.
2. Strategic Vendor Categorization and Segmentation
Not all vendors are created equal, and they shouldn't be managed that way. One of the most impactful vendor management best practices is strategic categorization, which involves classifying suppliers based on their importance, spend, and risk. This segmentation allows you to tailor your management style, allocating your most valuable resources to the vendors that matter most while creating efficient, streamlined processes for less critical partners.
This systematic approach moves beyond a one-size-fits-all model. By segmenting vendors, you can dedicate more time to nurturing strategic partnerships, negotiating performance-based contracts for preferred suppliers, and automating interactions with transactional vendors. This ensures you're investing your energy where it yields the highest return, strengthening crucial relationships and mitigating significant risks.
The hierarchy diagram below illustrates a common approach to vendor segmentation, classifying vendors into distinct tiers based on their business impact.
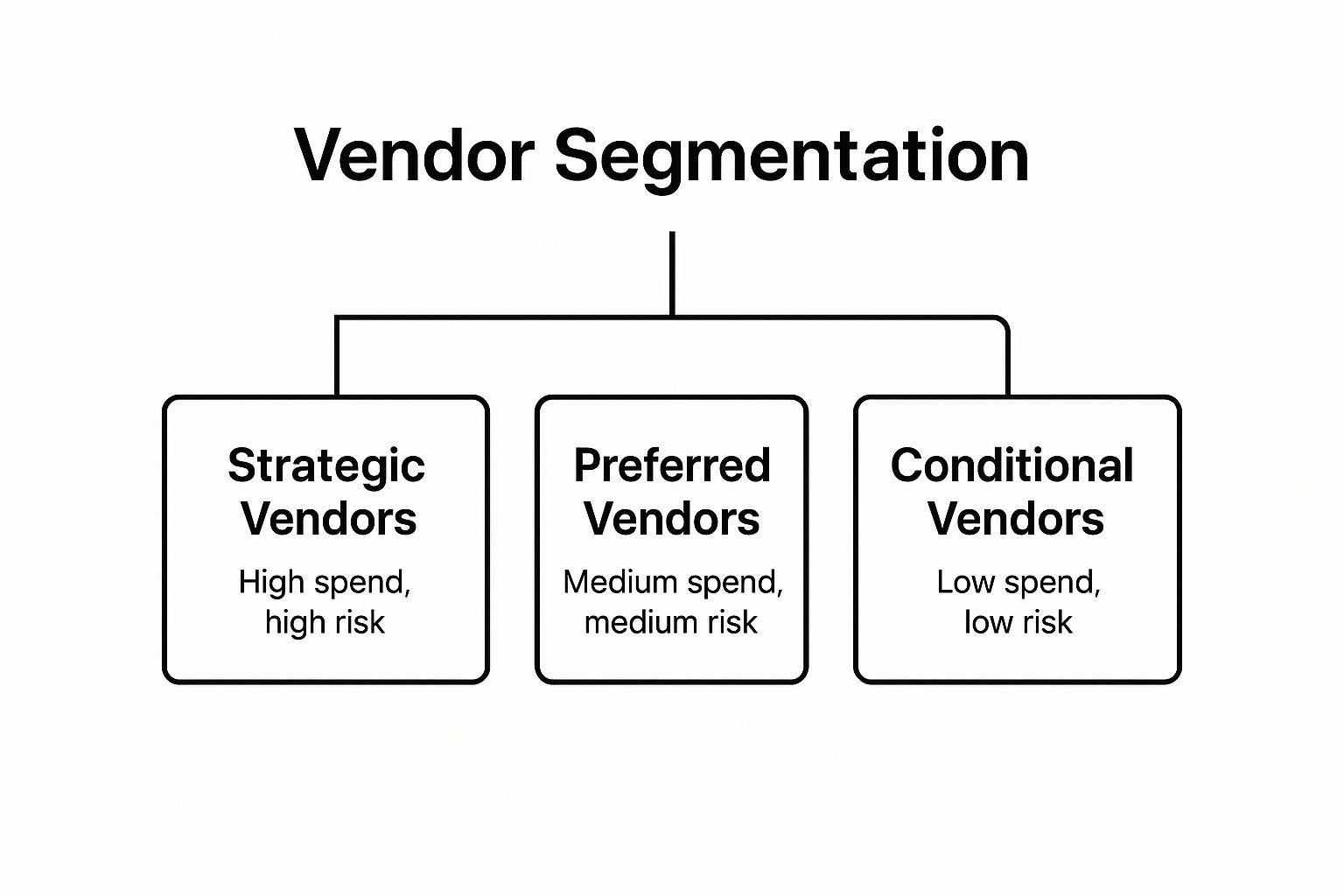
This tiered structure allows organizations to apply differentiated management strategies, focusing intensive resources on high-impact strategic vendors while maintaining efficiency with lower-tier suppliers.
Real-World Examples
- •Apple: The tech giant treats its core component suppliers like Foxconn as strategic partners, fostering deep integration and collaboration. In contrast, it uses competitive bidding for commodity components, demonstrating a classic segmentation strategy.
- •Procter & Gamble (P&G): P&G segments its suppliers to drive innovation. It identifies strategic partners for joint R&D and co-creation while managing thousands of other suppliers through more standardized, transactional processes.
How to Implement This Practice
- •Establish Clear Criteria: Define your segmentation criteria using a mix of factors like annual spend, business impact, risk level, and potential for innovation. Popularized by consultants like Peter Kraljic, this matrix approach is a proven starting point.
- •Use Data Analytics: Leverage procurement data to identify patterns and classify vendors objectively. Analyze spending trends and performance metrics to ensure vendors are in the appropriate category.
- •Differentiate Your Engagement Model: Create distinct service level agreements (SLAs), communication plans, and performance review cadences for each vendor tier. For example, hold quarterly business reviews with strategic vendors and only annual check-ins with conditional ones.
- •Review and Update Annually: Vendor relationships and business needs evolve. Re-evaluate your vendor segments at least once a year to ensure your categorization remains accurate and aligned with your overall business strategy.
3. Comprehensive Contract Management and Governance
Once a vendor is selected, the contract becomes the central pillar of the relationship. Comprehensive contract management is a structured approach to overseeing the entire contract lifecycle, from creation and negotiation to renewal or termination. This practice ensures compliance, monitors performance, and ultimately maximizes the value you get from your partnerships.
This goes far beyond just signing a document and filing it away. It involves creating a governance framework with standardized templates, clear ownership, automated workflows, and milestone tracking. By actively managing contracts, you protect your organization's interests, mitigate risks, and build a strong foundation for productive, long-term vendor collaborations.
Real-World Examples
- •Cisco: The tech giant uses a sophisticated contract management system to handle over 40,000 active contracts, leveraging automated workflows to ensure consistent compliance and operational efficiency.
- •Johnson & Johnson: With a global supply chain, it relies on a centralized contract repository to manage complex pharmaceutical agreements across more than 60 countries, ensuring uniformity and control.
How to Implement This Practice
- •Establish Clear Ownership: Assign a specific owner to each contract who is responsible for monitoring performance, managing timelines, and overseeing renewals. This creates accountability.
- •Create Contract Playbooks: Develop standardized guidelines and pre-approved clauses for your negotiation teams. This speeds up the process and ensures key protections are always included.
- •Track Key Milestones and Obligations: Use contract management software to set automated alerts for important dates like renewals, price adjustments, and performance reviews. This prevents missed deadlines and costly auto-renewals.
- •Define and Monitor KPIs: Embed key performance indicators (KPIs) directly into your contracts to measure value and performance. To maintain control over vendor deliverables and costs, it’s also essential to implement robust strategies for handling scope creep within your contracts.
- •Conduct Regular Health Checks: Periodically review active contracts to identify opportunities for optimization, renegotiation, or consolidation. Aligning contract terms with billing is also crucial, as detailed in our guide to invoice management best practices.
4. Performance Monitoring and Vendor Scorecards
Once a vendor is onboarded, the real work begins. Effective vendor management best practices demand a continuous, systematic approach to measuring performance. This is where vendor scorecards come in, providing a structured framework to track and evaluate vendor performance against predefined metrics and service-level agreements (SLAs).

Think of it as a report card for your suppliers. This data-driven approach moves you beyond gut feelings, enabling objective conversations about performance, identifying areas for improvement, and celebrating successes. By consistently monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), you can ensure you're getting the value you paid for and proactively manage the relationship for mutual benefit.
Real-World Examples
- •Toyota: The automotive leader uses a renowned supplier scorecard system that evaluates vendors on quality, delivery, technology, and management. This rigorous monitoring is a cornerstone of its legendary supply chain efficiency.
- •Dell: Its vendor performance management program tracks over 300 suppliers with detailed monthly scorecards, ensuring every partner aligns with its high standards for innovation and operational excellence.
- •Marriott International: The hospitality giant uses vendor scorecards for everything from IT services to marketing agencies, conducting quarterly business reviews to drive accountability and continuous improvement across its diverse vendor network.
How to Implement This Practice
- •Involve Vendors in KPI Definition: Collaborate with your vendors to define the metrics. This ensures the KPIs are fair, achievable, and aligned with both parties' goals, fostering buy-in from the start.
- •Balance Leading and Lagging Indicators: Don't just measure past results (lagging indicators like delivery time). Include forward-looking metrics (leading indicators like communication responsiveness) to predict future performance and prevent issues.
- •Use Data to Drive Collaboration: Frame performance discussions around objective data from the scorecards. This shifts the conversation from blame to a collaborative effort to solve problems and optimize outcomes.
- •Implement Tiered Performance Thresholds: Define clear performance tiers (e.g., excellent, acceptable, needs improvement) with associated consequences or rewards. This gamifies performance and incentivizes vendors to strive for excellence.
- •Regularly Review and Update Metrics: Business needs change. Review your scorecard metrics annually to ensure they remain relevant, effective, and aligned with your strategic objectives.
5. Centralized Vendor Management Office (VMO)
As your organization grows, managing vendors across different departments can become chaotic and inefficient. A centralized Vendor Management Office (VMO) acts as a dedicated hub for all vendor-related activities, policies, and relationships. This function standardizes processes, consolidates information, and ensures vendor management best practices are applied consistently across the entire enterprise.
Think of the VMO as the air traffic control for your vendor ecosystem. It provides a single source of truth, coordinates cross-functional activities, and drives strategic value from your supplier relationships. By centralizing oversight, you eliminate redundant efforts, reduce rogue spending, and gain a holistic view of vendor performance and risk, which is a cornerstone of effective vendor management best practices.
Real-World Examples
- •IBM: Its Global Procurement organization functions as a centralized VMO, managing over $40 billion in annual supplier spend and ensuring consistent standards for thousands of vendors worldwide.
- •Unilever: The consumer goods giant uses a centralized procurement function to strategically manage supplier relationships and drive innovation across more than 190 countries, ensuring alignment with its global sustainability goals.
How to Implement This Practice
- •Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Establish a clear charter that outlines the VMO's authority versus the business units' ownership. This prevents confusion and ensures smooth collaboration between central oversight and day-to-day operational needs.
- •Start with a Pilot Program: Before a full enterprise rollout, test the VMO concept within a single department or business unit. This allows you to refine processes, demonstrate value, and build momentum for broader adoption.
- •Invest in Change Management: A VMO represents a significant shift in how your organization works. Communicate the benefits clearly to all stakeholders and provide training to ensure everyone understands the new processes and their roles.
- •Establish Internal SLAs: Create service level agreements (SLAs) between the VMO and internal business units. This sets clear expectations for response times, support, and performance, treating internal teams like valued customers.
6. Vendor Relationship Management and Strategic Partnerships
Top-tier vendor management best practices extend beyond simple transactional exchanges. A strategic approach to vendor relationship management transforms key suppliers into true partners, fostering collaboration, innovation, and mutual growth. This involves moving from a purely cost-based mindset to one centered on value, trust, and shared objectives, creating a competitive advantage that can't be easily replicated.

Think of it as cultivating a business alliance rather than just managing a supplier. When you invest in building strong, transparent relationships with critical vendors, you gain access to their best ideas, priority service, and a willingness to solve problems collaboratively. This holistic approach unlocks long-term value and turns your supply chain into a powerful engine for innovation.
Real-World Examples
- •Nike & Apple: Their long-standing partnership resulted in the Nike+ product line, integrating technology and athletic wear in a way neither company could have achieved alone. This is a prime example of joint innovation driven by a strategic relationship.
- •Starbucks: The company actively invests in its coffee suppliers through its Farmer Support Centers, providing resources and training to ensure ethical sourcing and high-quality beans. This partnership secures their supply chain while upholding brand values.
How to Implement This Practice
- •Align Partnerships with Strategy: Identify vendors critical to your long-term business goals and focus your relationship-building efforts there. Beyond traditional vendors, fostering strategic partnerships can involve specialized professional services, such as when engaging legal consultants for complex regulatory matters.
- •Establish Clear Governance: Create a formal governance structure with defined roles, responsibilities, and clear escalation paths for resolving issues. This prevents misunderstandings and ensures accountability on both sides.
- •Create Joint Business Plans: Work with strategic partners to develop joint plans that include shared objectives, key performance indicators (KPIs), and success metrics. Regularly review progress together.
- •Invest in Relationship Training: Equip your vendor-facing teams with the skills needed to build and maintain strong professional relationships, focusing on communication, negotiation, and conflict resolution.
7. Digital Vendor Management Platforms and Automation
Manual vendor management is a recipe for inefficiency and human error. Embracing digital platforms and automation is one of the most impactful vendor management best practices you can adopt, transforming cumbersome processes into streamlined, intelligent workflows. These integrated solutions digitize everything from onboarding and contract management to performance tracking and payments, creating a single source of truth for all vendor-related activities.
Think of it as giving your vendor management program a central nervous system. Instead of chasing emails, spreadsheets, and paper documents, you gain end-to-end visibility and control. This shift not only saves countless hours of administrative work but also provides the data analytics needed for strategic decision-making, helping you identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and optimize spend.
Real-World Examples
- •Walmart: The retail giant leverages sophisticated supplier portals and automation to manage its massive network of over 100,000 suppliers globally, streamlining everything from inventory management to invoicing.
- •Airbus: The aerospace leader uses a complex supplier collaboration platform to manage its intricate supply chains across multiple countries, ensuring seamless coordination and compliance for highly specialized components.
How to Implement This Practice
- •Start with a Pilot Program: Instead of a full-scale rollout, begin with a small, focused pilot project. This allows you to prove the value of the platform, work out any kinks, and build momentum for broader adoption.
- •Prioritize User Experience: A platform is only effective if people use it. Focus on intuitive design and a positive user experience for both your internal teams and your vendors to drive engagement and ensure success.
- •Plan for Integration: Ensure the vendor management platform can integrate seamlessly with your existing enterprise systems, such as your ERP and accounting software. Robust integration is key to creating a truly unified data environment. Our guide on accounting process automation offers more insights into this.
- •Invest in Training and Change Management: Introduce the new system with comprehensive training and a clear change management plan. Communicate the benefits to all stakeholders to get them on board and ensure a smooth transition. To fully leverage these platforms, exploring various workflow automation examples can provide valuable insights into streamlining operations.
7 Key Vendor Management Practices Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor Risk Assessment and Due Diligence | High - time-intensive and expertise-heavy | High - specialized skills and tools needed | Mitigates risks, ensures compliance, improves vendor reliability | Organizations requiring deep vendor vetting and ongoing monitoring | Reduces risks, ensures compliance, informed decisions |
| Strategic Vendor Categorization and Segmentation | Medium - requires data analysis and maintenance | Medium - analytics tools and team effort | Optimized resource allocation, tailored strategies | Businesses managing diverse vendor portfolios for strategic focus | Improves negotiation, planning, management focus |
| Comprehensive Contract Management and Governance | Medium to High - technology and training needed | High - software investment and maintenance | Legal risk reduction, faster contract cycles, better spend control | Firms needing strict contract lifecycle control and compliance | Enhances compliance, accelerates workflows, improves accountability |
| Performance Monitoring and Vendor Scorecards | Medium - ongoing data collection and validation | Medium - automated tools and collaboration | Continuous performance improvement, objective vendor evaluation | Companies focusing on performance tracking and vendor improvement | Drives improvement, supports transparency and rewards |
| Centralized Vendor Management Office (VMO) | High - organizational change and process standardization | High - cross-functional coordination and systems | Consistent policies, consolidated spend, centralized oversight | Enterprises seeking enterprise-wide vendor management control | Reduces overhead, improves leverage, standardizes practices |
| Vendor Relationship Management and Strategic Partnerships | Medium to High - time and collaborative effort intensive | Medium to High - resource investment in relationship management | Strong partnerships, innovation, enhanced service levels | Organizations prioritizing strategic vendor collaboration | Drives innovation, builds trust, enhances continuity |
| Digital Vendor Management Platforms and Automation | High - tech implementation and system integration | High - software, integration, and training investment | Efficiency gains, real-time insights, faster onboarding | Enterprises aiming for digital transformation and process automation | Reduces manual work, improves accuracy, enables scalability |
Bringing It All Together: Your Path to Vendor Management Excellence
Navigating the world of vendor management can feel like a complex puzzle, but as we've seen, it's a puzzle you can solve with the right strategy. Moving beyond simple transactional relationships to build a strategic, value-driven vendor ecosystem is not just a lofty goal; it's a critical business advantage. By implementing these vendor management best practices, you transform a standard operational function into a powerful engine for growth, resilience, and innovation.
The journey starts with a solid foundation. Thorough risk assessments and due diligence ensure you're partnering with reliable and secure vendors from day one. From there, strategic vendor categorization allows you to focus your energy where it matters most, dedicating premium resources to your most critical partners while efficiently managing the rest.
From Tactical Tasks to Strategic Triumphs
Once the groundwork is laid, the focus shifts to nurturing and optimizing these relationships. Comprehensive contract management acts as your rulebook, ensuring clarity and compliance, while performance monitoring with vendor scorecards provides the data-driven insights needed for objective evaluation. This is where you can truly measure ROI and hold partners accountable.
However, the real magic happens when you combine structure with connection. Building strong, collaborative relationships and even a centralized Vendor Management Office (VMO) creates a culture of partnership. Instead of seeing vendors as mere suppliers, you begin to view them as extensions of your team, co-creating value and driving mutual success.
The Automation Advantage
Ultimately, the thread connecting all these best practices is efficiency. You can't focus on strategic relationship-building if your team is bogged down in manual, administrative work. This is the crucial role of digital transformation and automation.
Key Takeaway: True vendor management excellence isn't just about high-level strategy; it's about creating the operational space for that strategy to thrive. Freeing your team from tedious tasks like chasing invoices, manual data entry, and payment reconciliation is the first, most impactful step.
This is precisely where modern tools become indispensable. By automating the foundational, time-consuming aspects of vendor interactions, you unlock the human potential within your finance and operations teams. This shift allows them to concentrate on what they do best: analyzing performance data, negotiating better terms, and fostering the strategic partnerships that will define your company's future success. Embracing these vendor management best practices is your definitive roadmap to achieving that excellence.
Ready to build your vendor management strategy on a foundation of flawless automation? Discover how Tailride can eliminate manual invoice and receipt processing, giving your team the time and accurate data needed to focus on strategic growth. See the difference for yourself at Tailride.