7 Invoice Processing Best Practices for 2025
Discover 7 essential invoice processing best practices to streamline your AP workflow, cut costs, and boost efficiency. Unlock automation and accuracy today.
Tags

Invoice processing can feel like a constant battle. Between chasing down approvals, deciphering messy vendor invoices, and manually keying in endless lines of data, it’s a process ripe for errors, delays, and frustration. For many finance teams, it’s a major bottleneck that drains valuable time and resources, preventing them from focusing on more strategic work. The good news? It doesn't have to be this way. Transforming this cumbersome task into a streamlined, efficient, and even automated operation is entirely achievable.
The solution lies in implementing a set of proven invoice processing best practices. These aren't just abstract theories; they are actionable strategies that modern, high-performing companies use to cut costs, accelerate payment cycles, and significantly reduce the risk of fraud and human error. By adopting these methods, you can turn your accounts payable function from a reactive cost center into a proactive, data-driven asset for your organization.
This guide cuts straight to the chase, providing a detailed roadmap to optimize every step of your workflow. We will explore seven critical best practices, from implementing powerful automation and three-way matching to establishing crystal-clear approval hierarchies and maintaining pristine vendor data. You will learn not just what to do, but how to do it, with practical steps and real-world examples. Let’s dive into the strategies that will help you conquer invoice chaos, strengthen vendor relationships, and unlock new levels of financial control and efficiency.
1. Automated Invoice Processing
Kicking off our list is arguably the most transformative of all invoice processing best practices: automation. Ditching the mountains of paper and endless manual data entry is no longer a futuristic dream; it’s an accessible and crucial strategy for modern finance teams. Automated invoice processing uses technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to digitally capture, interpret, validate, and route invoices with minimal human oversight.
This practice fundamentally shifts your accounts payable (AP) workflow from a slow, error-prone cost center into a streamlined, strategic asset. Instead of manually keying in data from a PDF, the system automatically extracts key information like invoice number, vendor name, line items, and totals. It then validates this data against purchase orders and internal rules before sending it for approval, transforming a process that once took days into one that takes mere minutes.
How to Get Started with Automation
Implementing automation doesn't have to be an overwhelming overhaul. A phased approach is often the most successful.
- •Start with a Pilot Program: Begin with a select group of high-volume, standardized invoices from a few key vendors. This allows you to work out any kinks in a controlled environment.
- •Ensure Vendor Compliance: Work with your vendors to encourage the submission of digital-native invoices (like e-invoices or structured PDFs) rather than scanned paper copies. This dramatically improves data extraction accuracy.
- •Establish Exception Workflows: No system is perfect. Define a clear, efficient process for handling invoices that the system flags for review, such as those with mismatched POs or missing information.
- •Train Your Team: Automation changes roles from data-entry clerks to strategic reviewers. Provide thorough training on the new software and workflows to ensure a smooth transition and empower your team to manage the system effectively.
Key Insight: The goal of automation isn't to replace your AP team, but to empower them. By eliminating tedious manual tasks, you free up their time to focus on higher-value activities like vendor relationship management, cash flow analysis, and strategic financial planning.
The impact of automation is staggering, as seen in the success stories of major corporations. For example, Siemens slashed its invoice processing time from an average of 45 days down to just 5. Similarly, Coca-Cola European Partners now boasts a 95% straight-through processing rate, meaning the vast majority of their invoices are handled without any human touch at all.
This infographic breaks down the core benefits you can expect from adopting this approach.
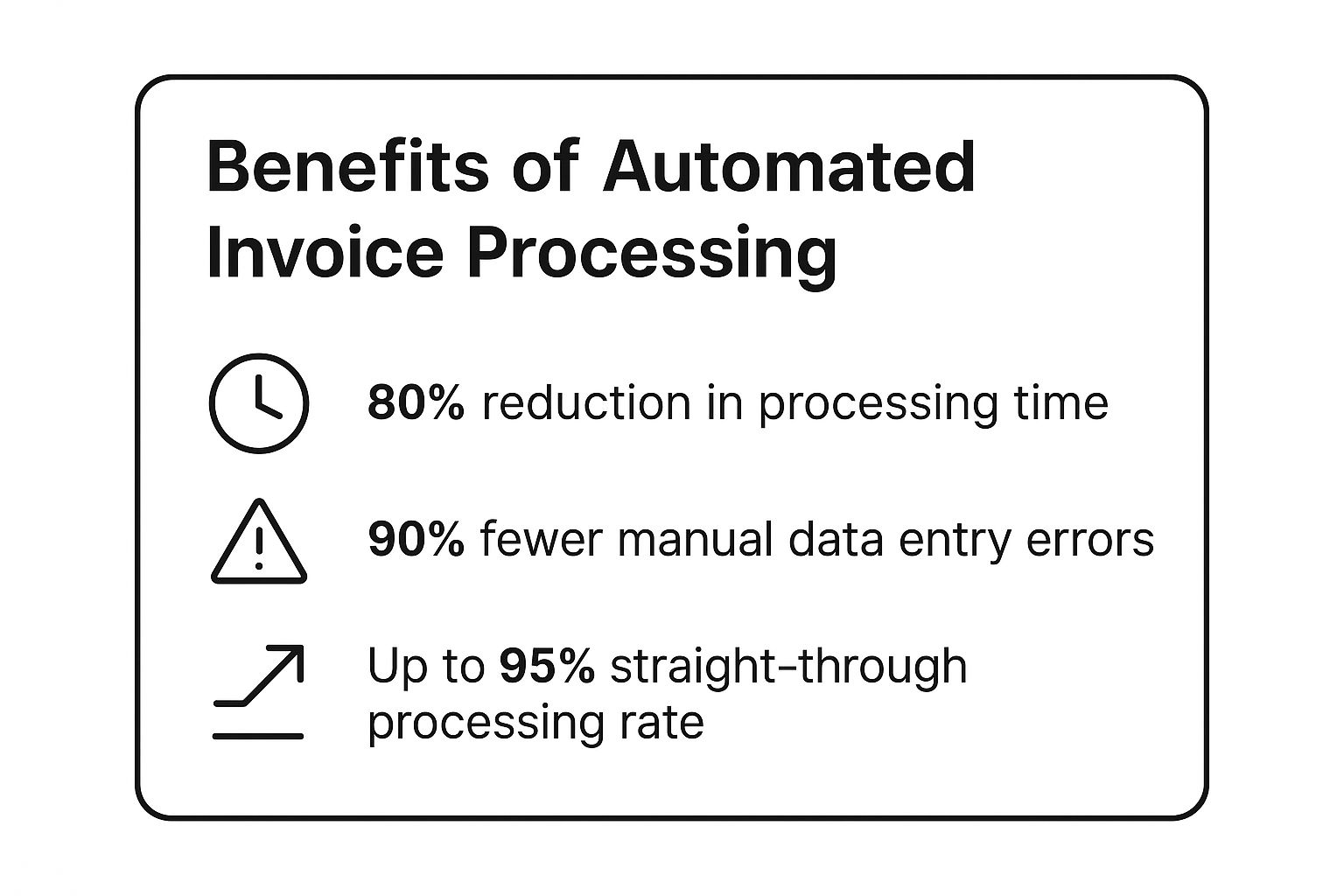
These metrics highlight a clear narrative: automation drastically improves speed, accuracy, and efficiency across the board. The reduction in manual errors alone saves countless hours in reconciliation and prevents costly overpayments.
For a deeper dive into how AI is revolutionizing invoice processing, check out this video:
By embracing automation, you’re not just adopting a new tool; you’re implementing one of the most powerful invoice processing best practices available to build a more resilient, efficient, and scalable finance operation.
2. Three-Way Matching
Following closely behind automation is one of the most fundamental yet powerful invoice processing best practices: three-way matching. This is a critical internal control process designed to prevent fraudulent payments, eliminate overpayments, and ensure you only pay for what you actually ordered and received. It involves meticulously comparing three key documents before any payment is released: the purchase order (PO), the goods receipt note (GRN), and the vendor's invoice.

This practice serves as your primary defense against invoice discrepancies. By verifying that the quantity, price, and terms on the invoice align perfectly with the initial purchase order and the subsequent delivery confirmation, you create a robust, auditable trail. This systematic check catches errors at the source, from incorrect pricing and duplicate invoices to phantom shipments that never arrived, safeguarding your company's cash flow and integrity.
How to Get Started with Three-Way Matching
Implementing a rigorous three-way matching process requires clear procedures and collaboration across departments, especially purchasing, receiving, and accounts payable.
- •Establish Clear Tolerance Levels: Decide on acceptable variance limits for price and quantity. For example, you might automatically approve an invoice if the total is within a 1% or $10 tolerance of the purchase order, which helps streamline the process for minor discrepancies.
- •Implement Automated Matching: Modern AP automation software can perform three-way matching instantly, flagging only the exceptions for human review. This drastically reduces manual effort and accelerates the approval cycle.
- •Create Streamlined Exception Handling: For invoices that fail the match, define a clear workflow. Who is responsible for investigating the discrepancy? What is the process for contacting the vendor or the purchasing department? A clear plan prevents bottlenecks.
- •Train Your Teams: Ensure that both purchasing and receiving staff understand the importance of creating accurate POs and promptly recording goods receipts. Their diligence is the foundation of an effective matching process.
Key Insight: Three-way matching isn't just a box-ticking exercise for the AP team; it's a strategic process that enforces discipline across the entire procurement-to-payment lifecycle. It fosters accountability and transparency from the moment an order is placed to when the final payment is made.
The value of this control is demonstrated by industry giants. For instance, General Electric successfully reduced its invoice processing errors by over 75% after implementing an automated three-way matching system. Similarly, Toyota's legendary supply chain relies on this principle to maintain quality control and payment accuracy with its vast network of suppliers. These examples show that mastering this practice is essential for building a scalable and secure financial operation. To discover more about the nuances of this control, learn more about the invoice matching process on tailride.so.
3. Electronic Invoice Submission
Following closely behind automation is another foundational pillar of modern AP: electronic invoice submission. This practice involves moving away from the costly and slow world of paper mail entirely. Instead, vendors submit their invoices through digital channels such as dedicated email inboxes, self-service web portals, or even direct system-to-system integrations like Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
By standardizing how you receive invoices, you eliminate the unpredictable delays and manual sorting associated with physical mail. This immediately accelerates the start of the processing lifecycle and dramatically reduces the risk of lost or misplaced documents. More importantly, receiving invoices in a digital format, especially as structured data, is a critical prerequisite for effective automation. This method transforms the first step of your AP workflow from a physical bottleneck into a seamless digital handoff.
How to Get Started with Electronic Submission
Transitioning your vendors to digital submission is a change management process that requires clear communication and support. A well-planned rollout will ensure high adoption rates.
- •Offer Multiple Submission Options: Cater to vendors of all sizes and technical capabilities. A simple dedicated email address (e.g., invoices@yourcompany.com) is easy for everyone, while a web portal or EDI integration offers more advanced functionality for high-volume suppliers.
- •Provide Clear Vendor Guidelines: During onboarding, give vendors explicit instructions on required formats (e.g., PDF, XML), necessary data points, and where to send their invoices. A simple one-page guide can work wonders.
- •Set Up Automated Confirmations: Configure an automatic email reply to acknowledge receipt of an invoice. This simple step provides vendors with peace of mind and significantly cuts down on "Did you get my invoice?" follow-up calls and emails.
- •Create a Vendor Self-Service Portal: For a more advanced approach, a portal where vendors can not only submit invoices but also track their payment status is invaluable. This empowers vendors and frees up your AP team from handling status inquiries.
Key Insight: The goal of electronic submission is to create a single, controlled, and digital "front door" for all incoming invoices. This standardization is a crucial step in building a predictable, efficient, and scalable accounts payable process.
The benefits of this shift are well-documented. The UK government, for example, mandated electronic invoicing for all public sector suppliers to streamline its procurement and payment cycles. Similarly, major corporations like Procter & Gamble and Amazon Business have made electronic submission a core part of their supplier networks, enabling them to process millions of invoices with superior speed and accuracy.
These examples underscore a vital point in our list of invoice processing best practices: controlling the intake of invoices is just as important as how you process them afterward. By embracing electronic submission, you lay the groundwork for a truly efficient and automated financial operation.
4. Centralized Invoice Processing
Next on our list of crucial invoice processing best practices is the strategic move to centralize your operations. For organizations with multiple departments, branches, or business units, invoices can often arrive in a chaotic, decentralized manner. Centralized invoice processing combats this by consolidating all invoice handling activities into a single, dedicated location or shared service center, creating a single source of truth for all things accounts payable.
This approach swaps fragmented, inconsistent workflows for standardized, streamlined procedures. Instead of each department having its own way of handling supplier bills, every invoice, regardless of its origin, is funneled to one expert team. This dramatically improves efficiency, enhances visibility, and gives management much tighter control over cash flow and vendor relationships across the entire organization.

This centralization lays the groundwork for further optimization, like automation, as it standardizes the inputs and processes that systems need to work effectively. It’s a foundational strategy championed by global consulting firms like Deloitte and PwC and successfully implemented by massive multinational corporations. For instance, Unilever centralized its invoice processing to serve 190 countries, and IBM’s Global Business Services handles invoices for countless business units worldwide, proving the model’s scalability and power.
How to Get Started with Centralization
Transitioning to a centralized model requires careful planning and communication to ensure a smooth and successful rollout.
- •Standardize Processes and KPIs: Before anything else, define a single, universal procedure for invoice submission, verification, and approval. Establish clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), such as "cost per invoice" and "days payable outstanding," to measure the success of your new centralized team.
- •Establish Clear Communication Channels: Create a robust system for your centralized team to communicate with individual business units and vendors. This includes setting up dedicated email addresses, phone lines, and regular reporting cadences to keep everyone informed and address queries promptly.
- •Invest in Staff Training and Development: Your centralized AP team members become specialists. Invest in training them not only on the new standardized processes but also on the specific needs of the different business units they will support.
- •Create Strong Vendor Onboarding: Develop a standardized process for onboarding new vendors that clearly communicates how and where they should submit all invoices. This prevents invoices from getting lost in old, decentralized channels.
Key Insight: Centralization isn't just about creating a single processing hub; it's about building a center of excellence. This specialized team develops deep expertise in payables management, leading to better fraud detection, improved vendor negotiations, and more strategic cash management.
The benefits of this model extend far beyond simple organization. By creating a single point of contact for all invoice-related matters, you reduce administrative overhead in other departments, allowing them to focus on their core functions. Johnson & Johnson famously implemented shared service centers for invoice processing across its many divisions, achieving significant cost savings and operational efficiencies.
This unified approach is a cornerstone of effective financial management. By adopting centralization, you are not just tidying up your workflow; you are implementing one of the most powerful invoice processing best practices for building a scalable, transparent, and highly efficient AP function.
5. Vendor Master Data Management
Next on our list of essential invoice processing best practices is the often-overlooked but critically important discipline of Vendor Master Data Management (MDM). Think of your vendor master file as the foundational "source of truth" for your entire procure-to-pay cycle. If this foundation is shaky, with duplicate entries, outdated information, or inconsistent data, it creates cracks throughout the process, leading to payment errors, compliance risks, and operational chaos.
Vendor MDM is the practice of creating and maintaining a centralized, accurate, and complete database of all your vendor information. This goes far beyond just a name and address; it includes crucial details like banking information, tax IDs (W-9s/W-8s), contracts, performance metrics, and contact details. A clean, well-managed vendor master file ensures every invoice is attributed correctly, payments are sent to the right accounts, and compliance checks are seamless.
How to Get Started with Vendor Master Data Management
Implementing a robust MDM strategy is a proactive measure that pays dividends in accuracy and security. It doesn't require a massive initial investment, just a commitment to process and governance.
- •Conduct Thorough Data Cleansing: Before anything else, audit your existing vendor list. Identify and merge duplicate entries, archive inactive suppliers, and verify critical information like banking details and tax IDs. This initial cleanup is crucial.
- •Establish Clear Data Governance: Define who is responsible for adding new vendors, updating existing information, and deactivating old accounts. Create a standardized vendor onboarding process with required fields and validation steps to prevent bad data from entering the system from the start.
- •Implement Automated Data Validation Rules: Use your ERP or accounting software to enforce data consistency. Set up rules that prevent the creation of a new vendor if a similar name or tax ID already exists. Automate checks to ensure bank account formats are correct and tax information is complete.
- •Integrate with Procurement and Financial Systems: Your vendor master data shouldn't live in a silo. Integrating it with your procurement and accounting platforms ensures that purchase orders and invoices automatically pull from the same verified source, drastically reducing manual entry and potential for error.
Key Insight: Strong Vendor MDM is your first line of defense against invoice fraud. A common fraud scheme involves tricking employees into changing a legitimate vendor's bank account details. A strict governance process, requiring multi-step verification for any changes to master data, effectively shuts down this risk.
Global giants have long recognized the power of this practice. Shell, for example, uses stringent vendor MDM to manage its massive network of thousands of suppliers across diverse business units, ensuring operational consistency and compliance. Similarly, the US Department of Defense implemented a vendor MDM system to streamline its complex procurement processes, leading to significant gains in efficiency and cost control.
By treating your vendor data as a strategic asset, you build a resilient framework that supports accurate and secure invoice processing. It’s a fundamental step toward creating a truly optimized and audit-ready accounts payable function.
6. Clear Approval Workflows
Next on our list of essential invoice processing best practices is the establishment of clear approval workflows. Simply put, this means creating a structured, transparent, and consistent process that dictates how an invoice moves from receipt to final payment authorization. It specifies who is responsible for approving invoices, under what conditions, and within what timeframes, eliminating bottlenecks and ambiguity.
Without defined workflows, invoices can get lost in email inboxes, sit on desks for weeks, or be approved by unauthorized personnel, leading to late payment penalties, damaged vendor relationships, and a significant risk of fraud. A well-designed approval workflow ensures that every invoice is reviewed and authorized by the right person at the right time, maintaining tight financial controls without sacrificing speed and efficiency.
How to Implement Clear Approval Workflows
Building effective approval workflows is about balancing control with agility. Here’s how to get started:
- •Design Role-Based Workflows: Structure your approval chains based on roles, departments, and financial thresholds. For instance, a marketing manager might be authorized to approve invoices up to $5,000, while anything higher automatically routes to the department head. This ensures proper oversight based on risk and value.
- •Implement Automated Routing: Leverage your AP software to automatically send invoices to the correct approver based on predefined rules. This eliminates the manual effort of forwarding emails and chasing down signatures, dramatically reducing processing delays.
- •Establish Clear Escalation Paths: What happens when an approver is on vacation or fails to respond? Define an automated escalation procedure that reroutes the invoice to an alternate approver or a manager after a set period, ensuring the process never stalls.
- •Enable Mobile Approvals: Modern business doesn't stop at the desktop. Provide managers with the ability to review and approve invoices on the go via a mobile app. This simple feature can significantly accelerate approval cycles, especially for remote or traveling team members.
Key Insight: Clear approval workflows are the guardrails of your AP process. They provide the necessary structure to prevent errors and fraud while using automation to ensure the process flows smoothly and quickly, rather than creating bureaucratic hurdles.
Companies that master this practice see remarkable results. For example, Google implements sophisticated, role-based approval workflows with automated escalation paths to manage its vast global expenditures efficiently. Similarly, Boeing uses multi-level approval processes tailored to different spending categories, ensuring rigorous oversight on high-value procurement while keeping routine purchases moving. These examples show that even at a massive scale, clarity in approvals is a cornerstone of financial integrity.
For a deeper look into streamlining this critical step, you can learn more about how to set up invoice approval automation.
By defining and automating your approval processes, you turn a potential chokepoint into a seamless and secure checkpoint. This is a fundamental step in building a robust system and one of the most impactful invoice processing best practices you can adopt for financial control and operational excellence.
7. Regular Process Audits and Monitoring
Next on our list of essential invoice processing best practices is a discipline that safeguards the integrity of your entire AP workflow: regular process audits and monitoring. Simply setting up a system isn't enough; you must continuously evaluate its performance to ensure compliance, catch inefficiencies, and prevent fraud. This practice involves a systematic review of your invoice processing activities, from data entry to final payment, to verify that they align with company policies and industry standards.
By embedding audits and monitoring into your operations, you transform your AP function from a passive participant into an actively managed and optimized system. Instead of waiting for a year-end review to uncover costly errors or process bottlenecks, you gain real-time visibility and periodic deep-dive analysis. This proactive approach helps identify issues like duplicate payments, policy non-compliance, or potential fraud before they escalate, ensuring your processes remain secure, efficient, and reliable.
How to Get Started with Audits and Monitoring
Integrating a robust audit and monitoring framework is a strategic move that builds resilience and drives continuous improvement.
- •Implement Monitoring Dashboards: Use your accounting or AP automation software to create real-time dashboards. Track key metrics like processing time per invoice, exception rates, and on-time payment percentages to get an at-a-glance view of your process health.
- •Schedule Formal and Surprise Audits: Conduct scheduled audits (e.g., quarterly or semi-annually) to perform a thorough review of a sample of invoices and transactions. Complement these with occasional surprise audits to ensure processes are being followed consistently, not just in preparation for a review.
- •Leverage Data Analytics: Go beyond simple spot-checks. Use data analytics to scan entire datasets for patterns and anomalies that could indicate systemic issues or fraudulent activity, such as multiple invoices with the same number or unusual payment amounts to a specific vendor.
- •Create Clear Action Plans: An audit’s value lies in its follow-up. For every finding, create a specific, time-bound action plan to address the root cause. Assign ownership for each action item to ensure accountability and track progress until resolution.
Key Insight: Regular audits are not about assigning blame; they are about fostering a culture of continuous improvement. They provide the objective feedback needed to refine workflows, strengthen internal controls, and adapt to changing business needs, ultimately making your AP process stronger and more efficient.
Leading companies demonstrate the power of this practice. For instance, American Express utilizes advanced data analytics to constantly monitor its vast invoice processing operations for anomalies, flagging potential issues in real time. Similarly, Walmart has implemented continuous monitoring systems for its vendor payment processes to minimize risk and ensure compliance on a massive scale.
These examples underscore a crucial point: consistent oversight is fundamental to maintaining a high-performing finance function. For those preparing for external scrutiny, creating a proactive internal audit system is key. You can find detailed guidance in our audit readiness checklist for growing businesses, which provides a structured approach.
By making regular audits and monitoring a core component of your strategy, you are not just checking boxes. You are actively implementing one of the most critical invoice processing best practices for building a transparent, accountable, and highly optimized financial operation.
7 Invoice Processing Best Practices Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Invoice Processing | High – involves AI, OCR, ERP integration, ongoing maintenance | High – technology investment, staff training | Up to 90% reduction in processing time; ~95% accuracy; fewer errors | High volume, standardized invoices; businesses seeking automation | Fast processing; error reduction; scalable; cash flow visibility |
| Three-Way Matching | Medium – requires robust data systems and defined procedures | Medium – staff training, system support | Prevents fraud and duplicates; ensures invoice accuracy | Organizations with strong internal controls; risk-averse companies | Strong control; reduces audit risk; improves vendor trust |
| Electronic Invoice Submission | Medium – setup of portals, digital formats, vendor onboarding | Medium – IT setup, vendor training | Eliminates postal delays; faster approvals; improved accuracy | Businesses digitizing vendor communication; remote/large vendor bases | Reduces paper costs; faster workflows; supports remote work |
| Centralized Invoice Processing | Medium – organizational change, standardization required | Medium – centralized team, communication infrastructure | Lower costs via economies of scale; improved consistency and control | Enterprises with multiple units needing unified processes | Cost savings; quality control; better audit trails |
| Vendor Master Data Management | High – extensive data cleansing, governance setup | Medium to High – data management, integration | Eliminates duplicates; improves payment accuracy; better vendor analysis | Large/global companies managing many vendors | Data consistency; risk reduction; supports sourcing decisions |
| Clear Approval Workflows | Medium – designing rules, automation, escalation mechanisms | Medium – workflow software, staff training | Reduces fraud risk; faster approvals; clear audit trails | Companies requiring strict control and compliance | Compliance; faster processing; budget management |
| Regular Process Audits & Monitoring | Medium to High – ongoing audit resources, advanced tools | Medium to High – audit teams, analytical systems | Detects fraud, errors; drives continuous process improvement | Organizations focused on compliance and process excellence | Early fraud detection; continuous improvement; performance data |
Putting Your Invoice Processing on Autopilot
We've explored a comprehensive suite of seven powerful strategies, each one a critical gear in the machine of a high-performing accounts payable department. From the game-changing efficiency of automated invoice processing and the robust security of three-way matching to the streamlined simplicity of electronic submissions, these aren't just isolated tips. They are interconnected pillars that support a truly modern, resilient, and strategic AP operation. Think of them less as a checklist and more as a blueprint for transforming a cost center into a value-driver.
Implementing these invoice processing best practices is a journey, not a destination. You’ve seen how centralizing your invoice intake, meticulously managing vendor data, defining crystal-clear approval workflows, and committing to regular process audits work together to create a system that is greater than the sum of its parts. The goal is to move beyond the reactive, paper-chasing scramble of traditional AP and into a proactive, data-driven future.
From Theory to Tangible Transformation
The real magic happens when you start weaving these threads together. Imagine a world where an electronic invoice arrives and is automatically captured and coded. This triggers an automated three-way matching process that verifies it against a purchase order and goods receipt note from your centralized system. Because your vendor master file is clean and up-to-date, there are no discrepancies to investigate.
The invoice then flows seamlessly through a pre-defined digital approval workflow, alerting the correct manager on their mobile device. Once approved, the payment is scheduled, and the entire transaction is logged for future audits, all with minimal human intervention. This isn't a futuristic fantasy; it's the tangible reality for businesses that commit to these best practices. This level of efficiency frees up your finance team to focus on strategic analysis, cash flow optimization, and building stronger vendor relationships, rather than drowning in administrative tasks.
Your Actionable Next Steps
Feeling inspired but a little overwhelmed? Don't be. The key is to start small and build momentum. You don't need to boil the ocean overnight.
- •Assess Your Current State: Begin by conducting a simple audit of your existing process. Where are the most significant bottlenecks? Are you losing invoices? Are late payment fees a recurring problem? Identify the one or two areas causing the most pain.
- •Prioritize Your First Initiative: Based on your assessment, pick one best practice to implement first. For many, embracing automated invoice processing provides the biggest and most immediate return on investment, as it lays the foundation for many other improvements.
- •Build a Business Case: Clearly articulate the benefits. Quantify the time saved, the potential reduction in errors, and the improved visibility. Show how investing in better invoice processing best practices will directly impact the bottom line and support overall business growth.
- •Embrace the Right Technology: Manual implementation can only get you so far. The true power of these practices is unlocked through automation. Look for solutions that can handle the entire lifecycle, from data capture to accounting system integration, to truly put your AP function on autopilot.
By adopting this methodical approach, you can systematically dismantle outdated, inefficient processes and replace them with a streamlined, automated, and audit-ready system. The result is more than just saved time; it’s enhanced security, better financial control, and a stronger, more scalable foundation for your company's future.
Ready to stop chasing paper and start implementing these best practices today? Tailride is the all-in-one platform designed to automate your entire invoice processing workflow, from inbox to accounting software. See how Tailride can help you build a world-class AP operation and give your team the tools they need to succeed.